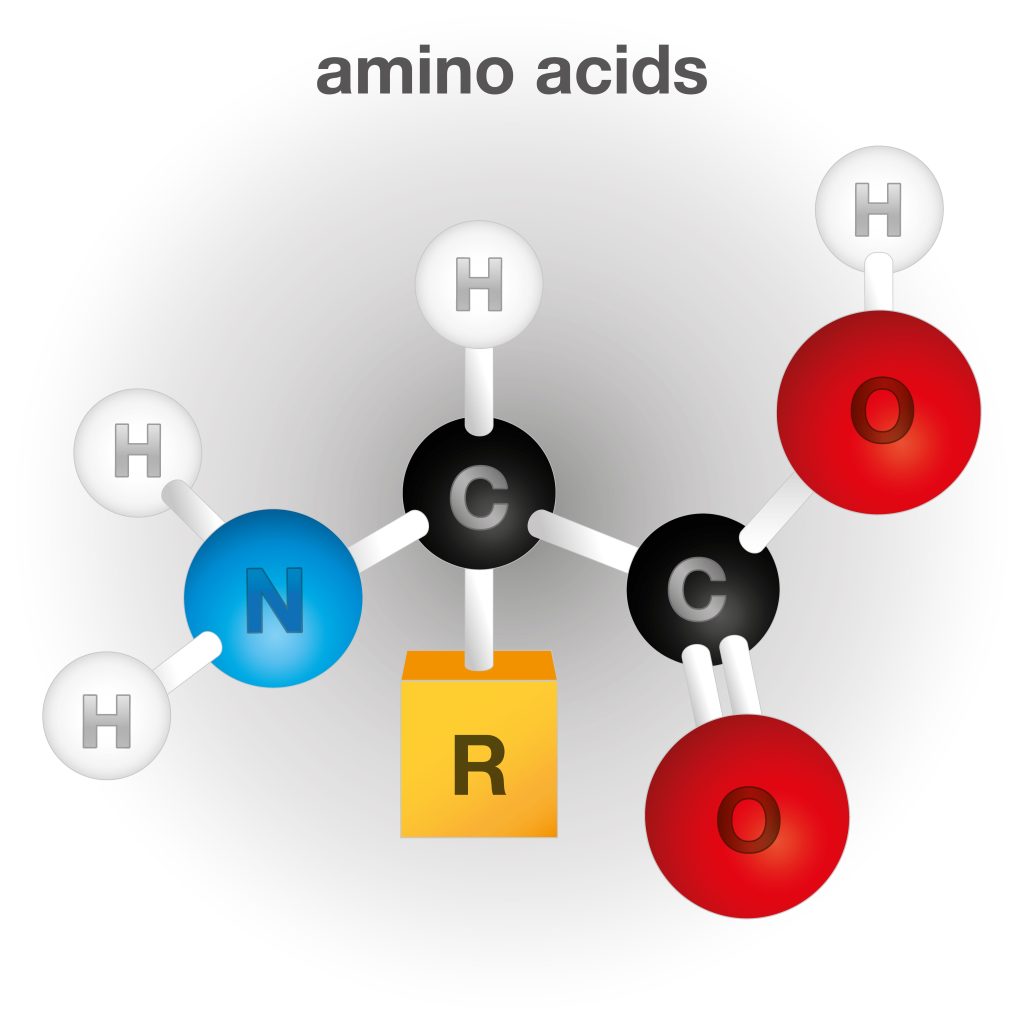
Amino acids are essential building blocks of proteins and play critical roles in various bodily functions. Here’s an overview of the essential amino acids and their key functions:
- Histidine: Important for neurotransmission, digestion, and immune response. It’s also a component of myelin, which protects nerve cells.
- Isoleucine: Essential for hemoglobin production, regulating energy levels, and supporting muscle metabolism.
- Leucine: Aids in protein synthesis, regulates blood sugar levels, and plays a role in growth hormone production.
- Methionine: Supports mineral absorption, detoxification processes, and is crucial for synthesizing proteins and DNA. It also contributes to the production of sulfur-containing molecules like cysteine and glutathione.
- Phenylalanine: Precursor to neurotransmitters like dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. It also plays a role in protein synthesis.
- Threonine: Essential for maintaining protein balance in the body, supporting immune function, and aiding in collagen and elastin production.
- Tryptophan: Precursor to serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates mood, appetite, and sleep. It’s also involved in protein synthesis.
- Valine: Supports muscle growth and repair, regulates blood sugar levels, and is one of the three branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs).
- Lysine: Important for calcium absorption, collagen production, enzyme synthesis, and immune function. It’s also essential for maintaining connective tissues.
These essential amino acids cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained through diet or supplementation. They are crucial for various physiological processes, from neurotransmission to muscle metabolism and immune function. While some can be found in abundance in animal products like meat, eggs, and dairy, others are present in smaller quantities in plant-based foods. Supplementation may be necessary for those with specific dietary restrictions or higher physical demands to ensure adequate intake of these vital nutrients.