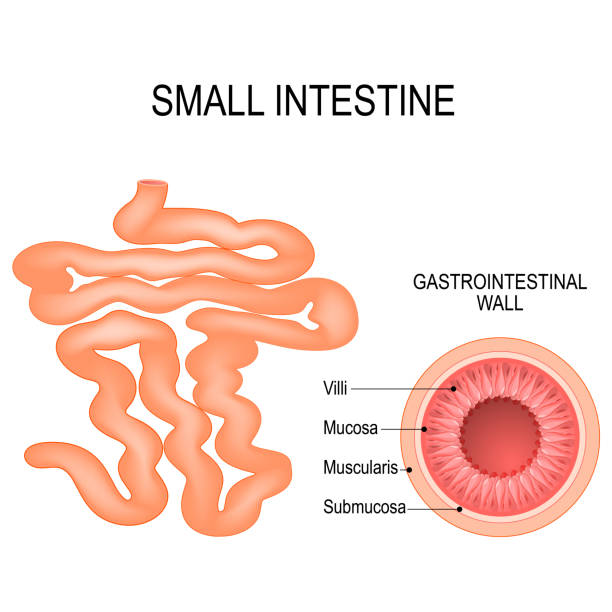
The small intestine is a vital organ responsible for digestion and nutrient absorption, spanning approximately 20 to 25 feet in length and coiled within the abdomen.
Anatomy and Function:
- Sections: Divided into three main parts – duodenum, jejunum, and ileum – each contributing to digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Digestive Processes: Receives digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the liver, aiding in the breakdown of food.
- Nutrient Absorption: Utilizes villi and microvilli to absorb nutrients such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, and minerals.
- Water Absorption: Processes approximately 7 to 11 liters of water daily, crucial for maintaining hydration and body function.
- Immune Function: Acts as a barrier against harmful bacteria and toxins, supporting immune health.
Common Conditions:
- Celiac Disease: Autoimmune disorder causing damage to the small intestine lining upon gluten ingestion.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Functional disorder affecting gut sensitivity, leading to pain, bloating, and irregular bowel movements.
- Crohn’s Disease: Chronic inflammation affecting any part of the gastrointestinal tract, often impacting the ileum.
- Intestinal Obstruction: Blockage preventing the passage of food or stool, requiring immediate medical attention.
- Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO): Abnormal overgrowth of bacteria in the small intestine, affecting nutrient absorption.
- Peptic Ulcers: Ulcers in the duodenum or stomach lining, often caused by H. pylori infection or excessive stomach acid.
- Short Bowel Syndrome: Resulting from surgical removal or damage to the small intestine, leading to nutrient malabsorption.
Maintaining Small Intestine Health:
- Healthy Lifestyle: Regular exercise and stress management to support digestive function.
- Hydration: Opt for clean, mineralized water from non-plastic sources to ensure proper hydration.
- Nutritious Diet: Choose unprocessed, contaminant-free foods to support optimal digestion and overall health.
Understanding the role of the small intestine in digestion and its susceptibility to various conditions underscores the importance of maintaining its health through lifestyle choices and appropriate medical care.